Level Up Your Git and GitHub Skills: Advanced Commands You Need to Master
Discover the Most Powerful Git and GitHub Commands that Will Take Your Skills to the Next Level
Advanced Command Used in Git and GitHub
As a developer, Git and GitHub are two essential tools that you use frequently. Git is a version control system designed to track changes in source code during software development while GitHub is a web-based repository hosting service that uses Git for version control. While learning the basics of Git and GitHub is vital, understanding advanced commands will take your skills to the next level. In this article, we will explore several advanced Git and GitHub commands you need to know.
In my previous blog, I have discussed the difference between Git and GitHub. Also made an introductory cheatsheet command for the Git CLI, Do check it the blog out here.
Let's start with the blog with the commands divide into different categories.
Knowing advanced commands can be helpful when working on a project with a team, as they can come in handy in certain situations. Therefore, it's a good idea to familiarize oneself with these commands and understand when they are appropriate to use.
1.📍Commonly Used Advanced Git Commands
A. git diff
The git diff the command is used to compare two different versions of the same file. For instance, you may want to compare the changes between your working directory and a commit. The git diff command is also useful in reviewing changes made by other team members. The following is an example of how to use the git diff command:
git diff <source_branch> <target_branch>
B. git stash
The git stash the command is used to save changes temporarily. Sometimes you may want to switch to another branch, but you're not ready to commit the current changes. In such cases, you can use git stash to save the changes temporarily, switch to another branch, and restore the changes later. The following is how to use git stash command:
git stash
C. git rebase
The git rebase command is used to merge changes from one branch to another branch while maintaining a linear history. You can use git rebase to pull upstream changes from a remote repository before pushing your changes. It's always recommended to use git rebase instead of git merge to keep your history clean. The following is an example of how to use the git rebase command:
git checkout target_branch
git rebase source_branch
D. git cherry-pick
The git cherry-pick command is used to apply commit changes of another branch to the current branch. It's useful when you want to apply a specific fix or feature from another branch. The following is an example of how to use git cherry-pick command:
git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
E. git bisect
The git bisect command is used when there's a need to locate which commit caused a bug. It's a binary search algorithm that helps you identify the offending commits. The following is an example of how to use the git bisect command:
git bisect start
git bisect bad <commit-hash>
git bisect good <commit-hash>
2. 📍Advanced GitHub commands
A. git submodule
The git submodule command is used to manage code libraries used in a GitHub repository. Submodules help you manage other programs or libraries as separate projects inside your repository. The following is an example of how to use git submodule command:
git submodule add <repository>
B. git amend
The git amend command is used when you want to modify the latest commit. For instance, you can use git amend to modify your commit message or add missing changes to the latest commit. The following example demonstrates how to use git amend command:
git commit --amend
C. git reflog
The git reflog command is used to identify lost commits. It records all the changes that happen to the Git repository, even if some commits are removed. The following is an example of how to use the git reflog command:
git reflog
D. git blame
The git blame command is used to track changes to a file. The command shows every line of code, with the name of the developer who last edited it and the commit message. It's useful in understanding who changed code and why. The following is an example of how to use the git blame command:
git blame <filename>
3. 📍Best Practices for Using Advanced Git Commands and GitHub
A. Proper Usage of Advanced Commands
Although advanced Git commands and GitHub commands are useful, misusing them can result in serious consequences. Before using advanced commands, ensure that you understand them, and only use them when it's necessary.
B. Understanding the Risks of Advanced Commands
Advanced Git commands and GitHub commands come with risks such as corrupting repositories or losing commits. Ensure that you're aware of the risks, and you're comfortable with the possibility of losing data.
C. Creating Backups and Restoring Commits
Always create backups of your repositories before running commands that could cause data loss. In case something goes wrong, you can restore the lost commits.
D. Always Reading the Documentation
Ensure that you regularly read Git and GitHub documentation, especially when using advanced commands. The documentation is always updated as new features are released.
4. 📍Bonus Section ✨
Above mentioned commands such as rebase, stash, and diff come in handy when you face the "Merge Conflict Problem". Below is an real-life example i have face for merge conflict and how you can avoid it and most importantly resolve it
What is Merge Conflict 🤔???
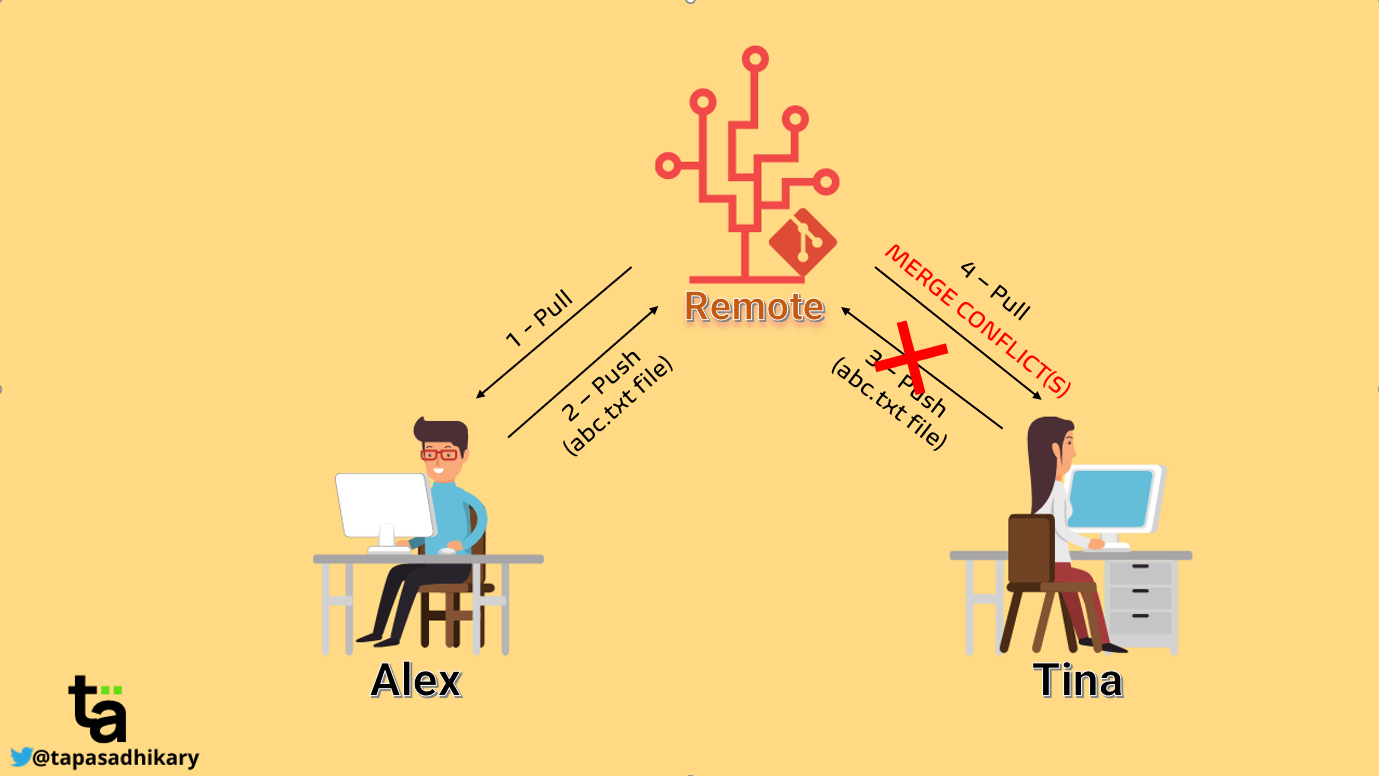
Merge conflict is a common occurrence when working collaboratively on a codebase. It happens when two or more people modify the same part of a file, resulting in conflicting changes that Git can't automatically resolve.
Resolving merge conflicts can be intimidating, but it's not as complicated as it sounds. The first step is to identify the conflicts and understand the changes made by each person. Once you know what's causing the conflict, you can make a decision on which changes to keep and which to discard.

To resolve the conflict, you can use a merge tool like the vs code supports inbuilt merge tool, or you can manually edit the files in question to remove the conflicting lines. Once the conflict is resolved, you can commit the changes and push them to the repository.
The key to successfully resolving merge conflicts is clear communication and collaboration with your team. By staying in sync and communicating about changes, you can minimize the chances of conflicts arising in the first place.
At last, cheatsheet are a great way to revise concepts and will always help for quick reference in future
CHEATSHEET FOR ADVANCED GIT COMMANDS
| Command | Description |
| git diff | Compare two different versions of the same file. |
| git stash | Save changes temporarily when switching to another branch. |
| git rebase | Merge changes from one branch to another while maintaining a linear history. |
| git cherry-pick | Apply commit changes of another branch to the current branch. |
| git bisect | Locate which commit caused a bug. |
| git submodule | Manage code libraries used in a GitHub repository. |
| git amend | Modify the latest commit, such as the commit message or adding missing changes. |
| git reflog | Identify lost commits and record all changes that happen to the Git repository, even if removed. |
| git blame | Track changes to a file and show every line of code, with the name of the developer and message. |
5. 📍Conclusion
Git and GitHub are essential tools for developers. It's vital to understand the advanced commands necessary to take your skills to the next level. In this article, we have explored several advanced Git and GitHub commands you need to know. Always ensure that you follow best practices when using advanced Git commands and GitHub.
